The medical insurance system refers to a mechanism by which a country or region collects, allocates, and utilizes medical insurance funds following insurance principles to address residents' healthcare needs. It serves as an effective financing mechanism for public healthcare, represents an advanced component of social security systems, and stands as a widely adopted global model for managing healthcare expenditures.
China's basic medical security framework comprises the Urban Employee Basic Medical Insurance, Urban Resident Basic Medical Insurance, New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme, and Urban-Rural Medical Assistance System. Since 1997, governmental efforts to strengthen this framework have achieved breakthrough progress, establishing the world's largest medical security system. Nevertheless, challenges persist due to China's vast population and regional economic disparities, including overall inadequate coverage levels, significant benefit disparities across population groups, insufficient adaptability to mobility, and sustainability concerns.
Concurrently, medical security and healthcare services are intrinsically linked and mutually reinforcing—medical security functions must be realized through purchasing healthcare services, while this purchasing process also propels healthcare system development. On one hand, the continuous improvement of the medical security system provides stable funding for national health, which ultimately transforms into healthcare institution revenue through service procurement, thereby supplying a steady financial foundation for healthcare development. On the other hand, as representatives of insured populations, medical security institutions exercise supervisory, constraining, and guiding roles over medical institutions during service procurement. This facilitates external checks-and-balances mechanisms, standardizes medical service practices, and promotes healthcare system reforms and enhanced institutional management.
To support related research, CnOpenData releases Designated Medical Insurance Service Institutions Data, encompassing nationwide designated medical institutions, designated retail pharmacies, and medical insurance administrative bodies. To facilitate scholarly use, CnOpenData precisely identifies latitude and longitude coordinates of medical institutions in each table and provides formatted administrative divisions at provincial, municipal, and county levels.
Time Coverage
As of 2023.01.31 (updatable upon request)
Data Scale
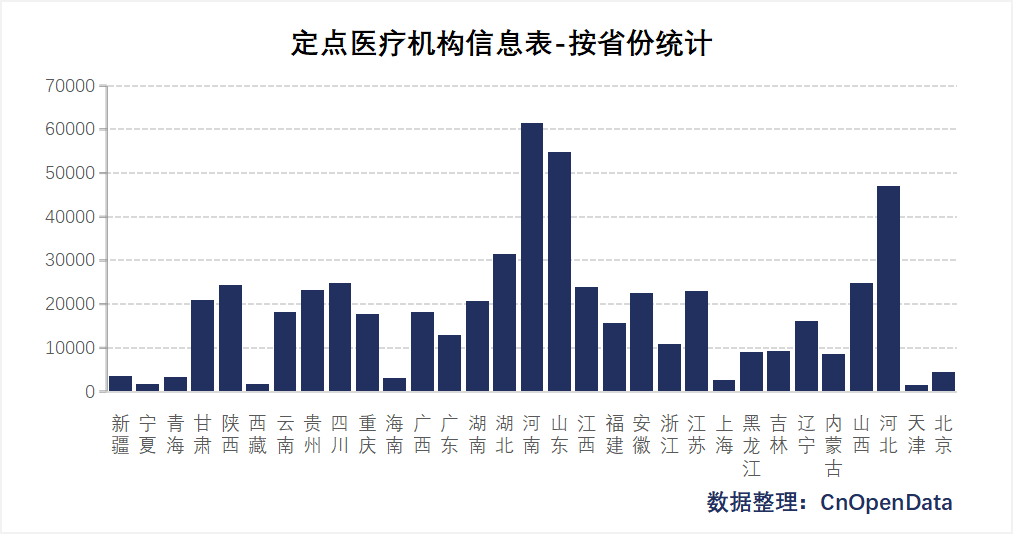
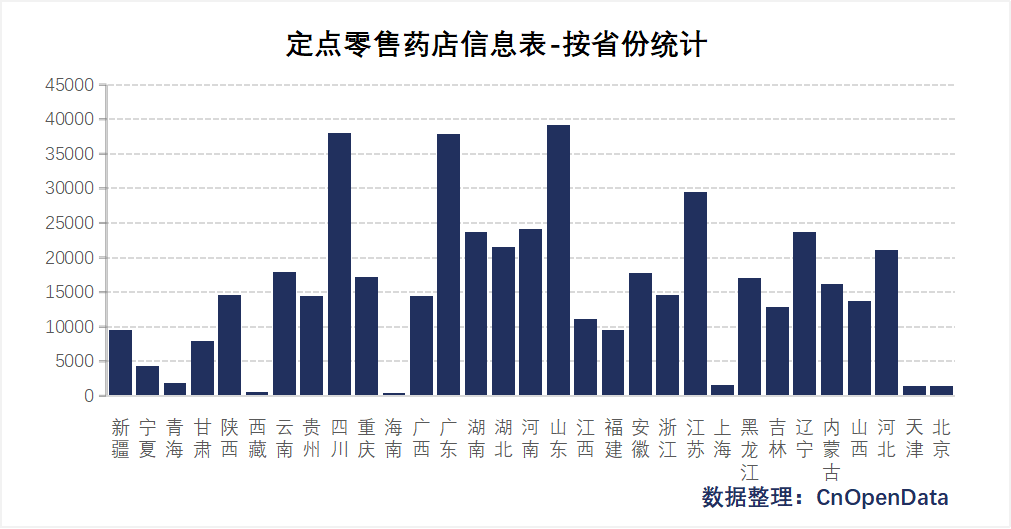
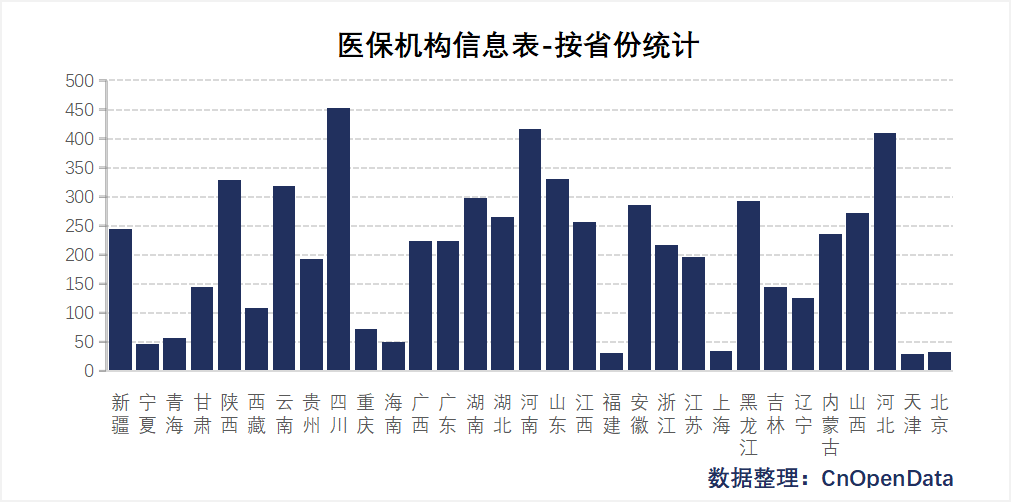
Field Display
Sample Data
Given the multi-table structure of this dataset, partial tables are displayed on this page. For full details, please refer to the left sidebar sub-tables.
定点医疗机构信息表
定点零售药店信息表
医保机构信息表
Data Update Frequency
Annual updates