& The Chinese Enterprise Environmental Administrative Penalty Database System compiles environmentally-related administrative penalty records publicly disclosed by ecological environment authorities at all levels in China, covering corporate violation information across all provinces, municipalities, and districts (counties) nationwide. This database contains over twenty fields including Announcement Date, Penalized Entity Name, Region, Penalty Type, Penalty Outcome, Fine Amount, Violation Type, Violation Content, Handling Authority, Relevant Regulations, and Industry Classification, comprehensively reflecting corporate environmental compliance performance and regulatory dynamics. The data is updated annually, making it suitable for long-term trend analysis and cross-regional comparative studies.
Data Features:
- Comprehensive Coverage with Strong Geographical Penetration: Data spans all 31 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government, with granular details down to municipal, district (county) levels, supporting multi-level geographical analysis and regional comparative studies.
- High Structural Integrity Facilitating In-depth Mining: Beyond basic penalty information, it includes four-tier industry classification (sector, major category, medium category, minor category), as well as fields such as violation type, violation specifics, and relevant regulations, enabling industry compliance profiling and policy impact assessment.
- Temporal and Institutional Dimensions Supporting Dynamic Tracking: The "Announcement Date" and "Penalty Date" fields allow users to trace temporal patterns of penalty enforcement and information disclosure. The "Handling Authority" field facilitates analysis of enforcement preferences and intensity across regulatory bodies.
Data Application Value:
- Academic Research Support: Applicable to environmental policy evaluation, research on the correlation between corporate environmental behavior and economic performance, comparative studies of environmental justice and administrative enforcement, providing high-quality panel data for empirical analysis.
- Reference for Government and Regulatory Agencies: Useful for monitoring regional environmental enforcement intensity, identifying high-frequency violation industries and behaviors, evaluating policy implementation effectiveness, and informing environmental target setting and enforcement resource allocation.
- Corporate Compliance and Risk Management: Enterprises can conduct self-inspections against industry-specific high-frequency violations to identify potential compliance risks. Investors and partners may leverage this data to assess target companies' environmental responsibility fulfillment.
- Green Finance and ESG Investment: This database provides financial institutions and rating agencies with corporate environmental penalty records, serving as a critical data source for ESG ratings, green credit approvals, and investment risk control.
The CnOpenData Chinese Enterprise Environmental Administrative Penalty Database is compiled from publicly available information disclosed by ecological environment authorities at all levels, ensuring high authority and completeness. It not only offers researchers a micro-level perspective on China's environmental governance and corporate environmental conduct but also provides governments, enterprises, and financial institutions with a solid data foundation for environmental risk management and decision-making. We believe this database will actively promote environmental compliance awareness and contribute to green development and sustainable investment.
Time Range
2000-2025 (updatable as needed)
Data Scale
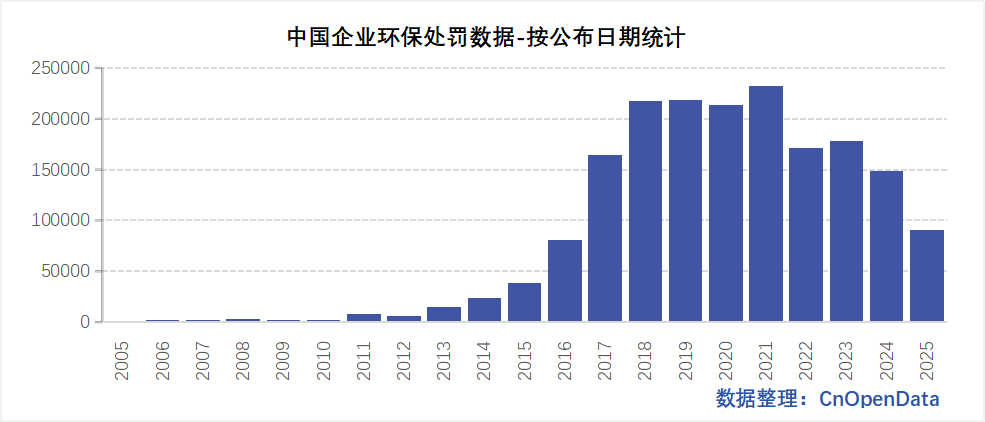
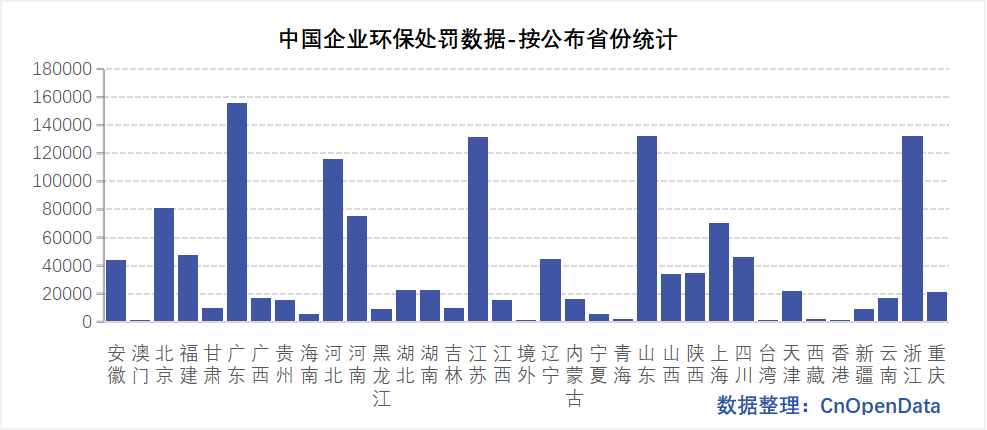
Field Display
Sample Data
Related Literature
- Kong, Dongmin and Liu, Chenhao, 2023, "Centralization and Regulatory Enforcement: Evidence from Personnel Authority Reform in China ", Journal of Public Economics, forthcoming.
- Ke Shaojing, Ma Ouyang, Xu Nianxing, 2023: "Spillover Effects of Competitors' Environmental Penalties: A Corporate Green Innovation Perspective", Journal of Management Sciences in China, No. 6.
Data Update Frequency
Annual Update
