On January 21, 2020, the National Health Commission issued Announcement No. 1, classifying pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus as a Class B infectious disease under the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, while implementing Class A prevention and control measures. Currently, COVID-19 prevention remains at a critical stage, where nucleic acid testing as a diagnostic tool plays a vital role in rapid diagnosis, efficacy evaluation, and epidemic containment.
- Timely nucleic acid testing. Given the emergent nature of COVID-19 and its evolving variants—some characterized by rapid transmission, high infectivity, and stealth spread—prompt screening is essential.
- Repeated nucleic acid testing. Due to challenges such as viral incubation periods, detection window limitations, and sampling variability, multiple rounds of testing are necessary to identify positive cases. Repeated monitoring of viral load changes provides critical indicators for predicting treatment efficacy and recovery status.
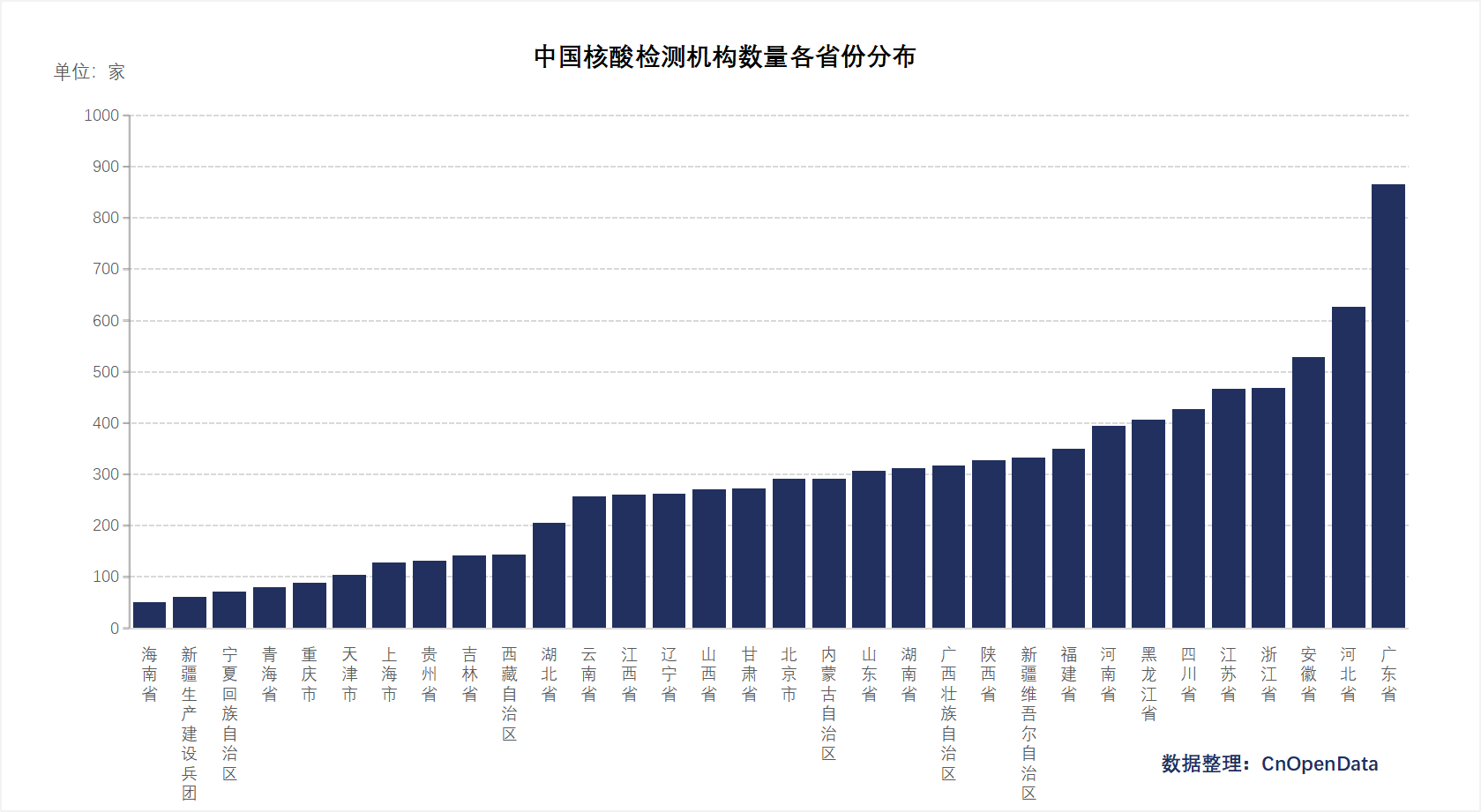
To ensure nucleic acid testing and medical services under normalized epidemic prevention, the National Health Commission has established dedicated nucleic acid testing institutions nationwide. Additionally, given China's large population and high mobility, nucleic acid sampling sites serve as crucial buffers during sudden outbreaks of new variants, balancing the "dynamic zero-COVID policy" with societal needs in the absence of robust infrastructure.
CnOpenData has compiled comprehensive information on testing institutions and sampling sites across 31 provinces and municipalities in China, providing foundational support for future epidemic research and clinical efforts.
Field Descriptions
Data Scale
Time Coverage
As of October 2022
Sample Data
Nucleic Acid Testing Institutions Table
Nucleic Acid Sampling Sites Table
Update Frequency
Updated irregularly
