Law refers to a system of behavioral norms formulated or recognized by the state and enforced through state coercive power. It reflects the will of the ruling class determined by specific socio-economic conditions, defines rights and obligations, and aims to establish, protect, and develop social relations and order favorable to the ruling class. The term "law" can be understood in both broad and narrow senses. Broadly, it encompasses all normative documents; narrowly, it refers specifically to normative documents enacted by the National People's Congress (NPC) and its Standing Committee. Regulations denote normative documents formulated by state organs, such as administrative regulations promulgated by the State Council of China and local regulations enacted by provincial, autonomous regional, or municipal people's congresses and their standing committees.
As a vital component of the legal system, local regulations differ fundamentally from local government rules:
- First, the promulgating authorities differ;
- Second, their authority and social effects differ. Local government rules possess lower legal force than local regulations. Local regulations are effective within their respective provinces (or municipalities) but hold lesser force than the Constitution, national laws, administrative regulations, and local regulations of their provinces or autonomous regions.
The China Legal and Regulatory Database launched by CnOpenData encompasses four modules: national laws, administrative regulations, local regulations, and judicial interpretations. It includes fields such as title, enacting authority, legal nature, effective date, and full text. The data covers three legal statuses: valid, amended, and repealed.
Time Period
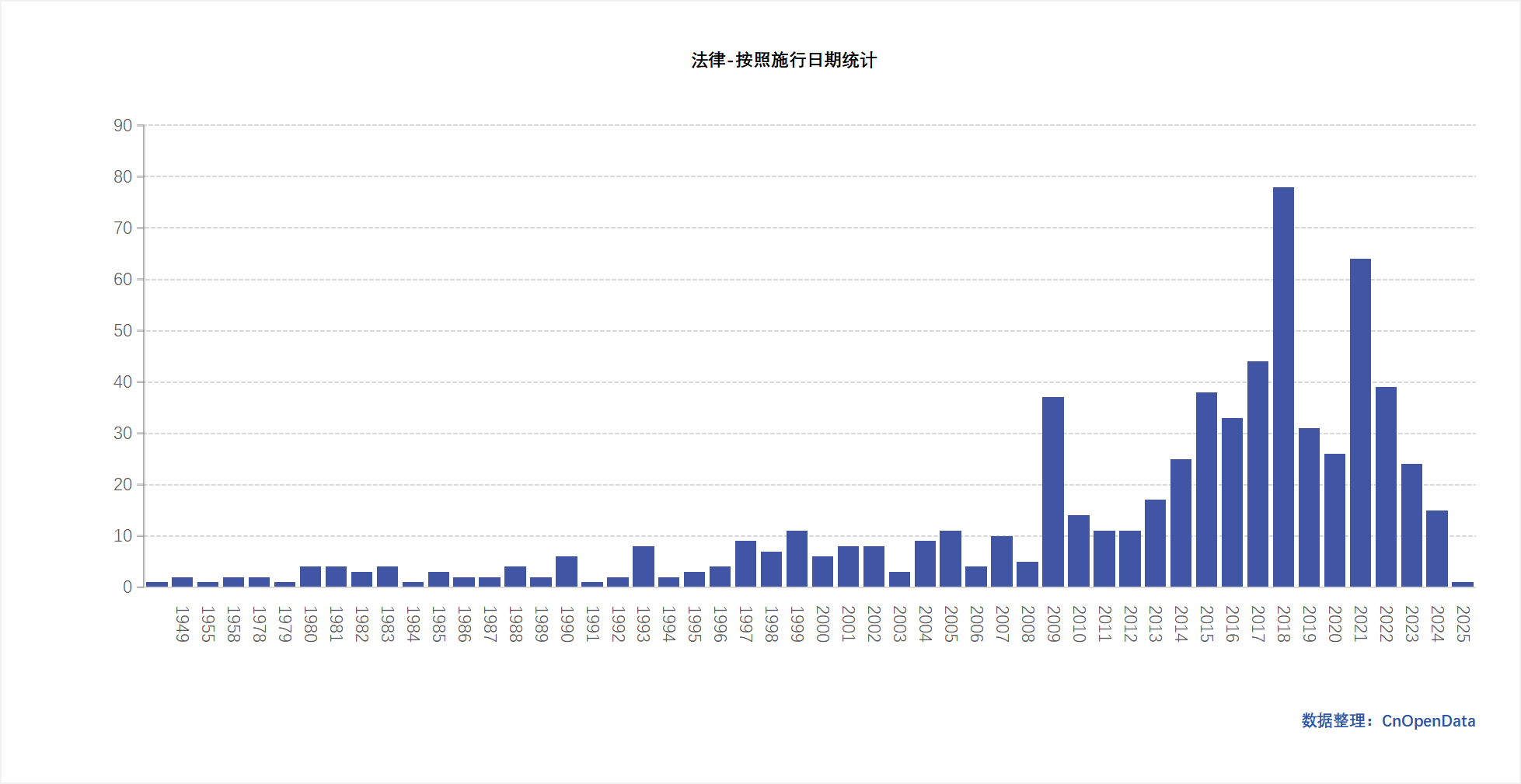
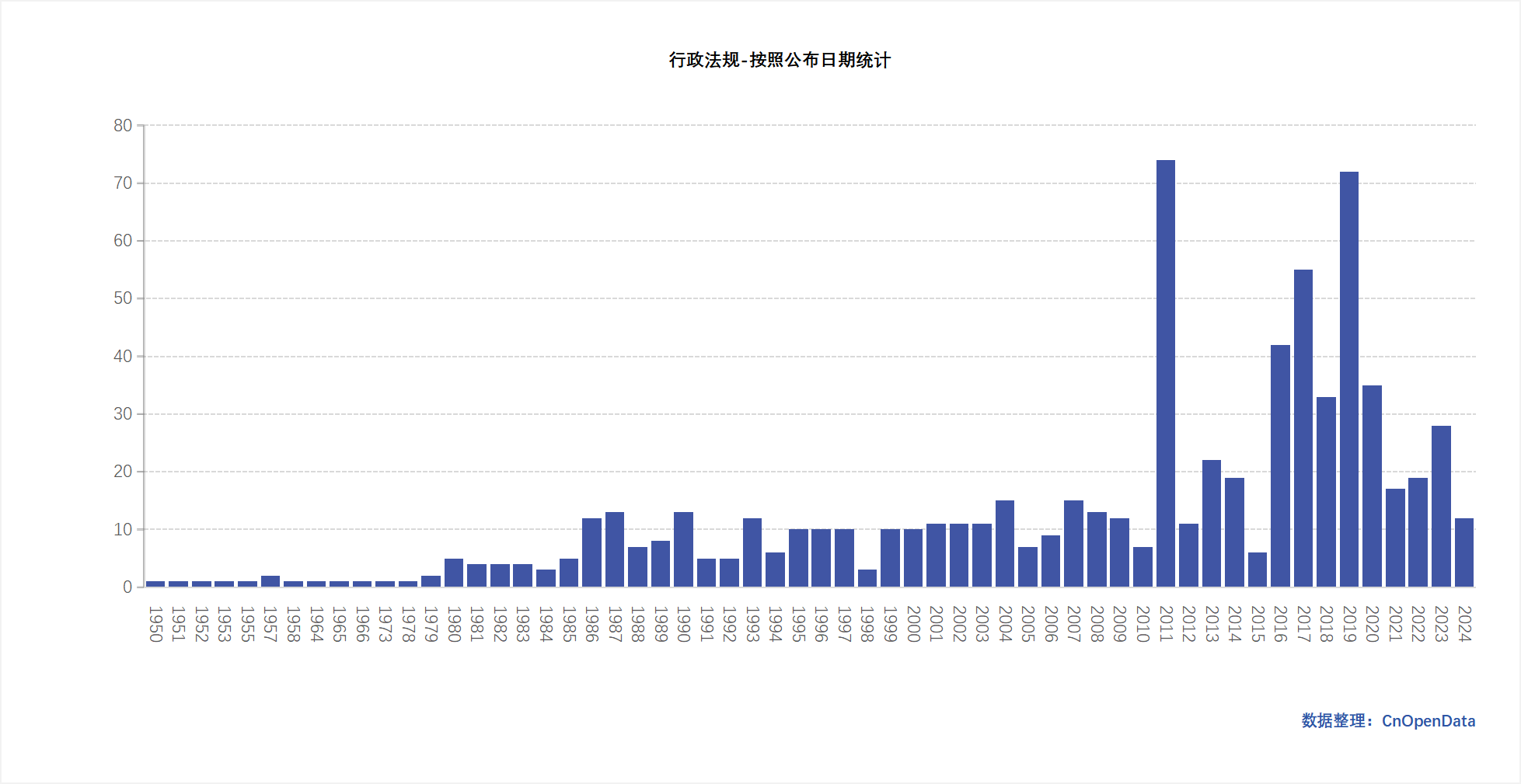
1950–June 2024. Specific time ranges for different legal documents are detailed in respective tables. (Updatable as needed)
Data Scale
Field Display
Sample Data
Laws (法律)
Administrative Regulations (行政法规)
Local Regulations (地方性法规)
Judicial Interpretations (司法解释)
Related Literature
- Liu Yida, 2023: "The Position of Supervisory Regulations in China’s Legal System," Administrative Law Review, No. 2.
- Zhao Jianwen, 2010: "The Status of International Treaties in China’s Legal System," Chinese Journal of Law, No. 6.
Data Update Frequency
Annual updates
