Following the Reform and Opening-up, China transitioned significantly from a planned economy to a market economy. On one hand, coastal cities implemented more flexible policies to attract foreign investment for establishing factories and enterprises. On the other hand, the relaxation of the household registration system increased government tax revenue, promoted employment, and facilitated the acquisition of relevant experience and technology from foreign-funded or joint ventures, thereby fostering the development of domestic enterprises and their affiliated industries.
Against this historical backdrop, numerous new companies emerged, survived, and achieved sustained growth. However, risks concurrently arose, with some enterprises engaging in fraudulent activities under various pretexts. Due to information asymmetry, stakeholders struggled to distinguish genuinely sound enterprises from high-risk entities with underlying issues. To address this, the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) mandated the public disclosure of enterprise information, substantially enhancing corporate transparency. Such disclosures encompass not only primary business classifications, registered addresses, registered capital, and registration dates but also extensive data on intellectual property, defaulters, and risk warnings. This provides exceptional research support for analyzing corporate survival, industry coverage, and market vitality in China.
This release by CnOpenData presents highly valuable and comprehensive information on Chinese industrial and commercial registered enterprises, totaling over 170 million records. Centered on enterprises registered annually, the dataset includes over a hundred fields such as Unified Social Credit Code, registration date, registered capital, corporate patents, and judicial documents. It spans five key dimensions: Basic Information, Key Focus Areas, Intellectual Property, Enterprise Development, and Operational Status. These dimensions encompass but are not limited to the displayed tables and field indicators, offering full coverage of corporate operational information.
Given the dataset’s multi-table structure, CnOpenData illustrates hierarchical relationships and dependencies in the data schema to facilitate comprehension.
Articles Citing This Dataset
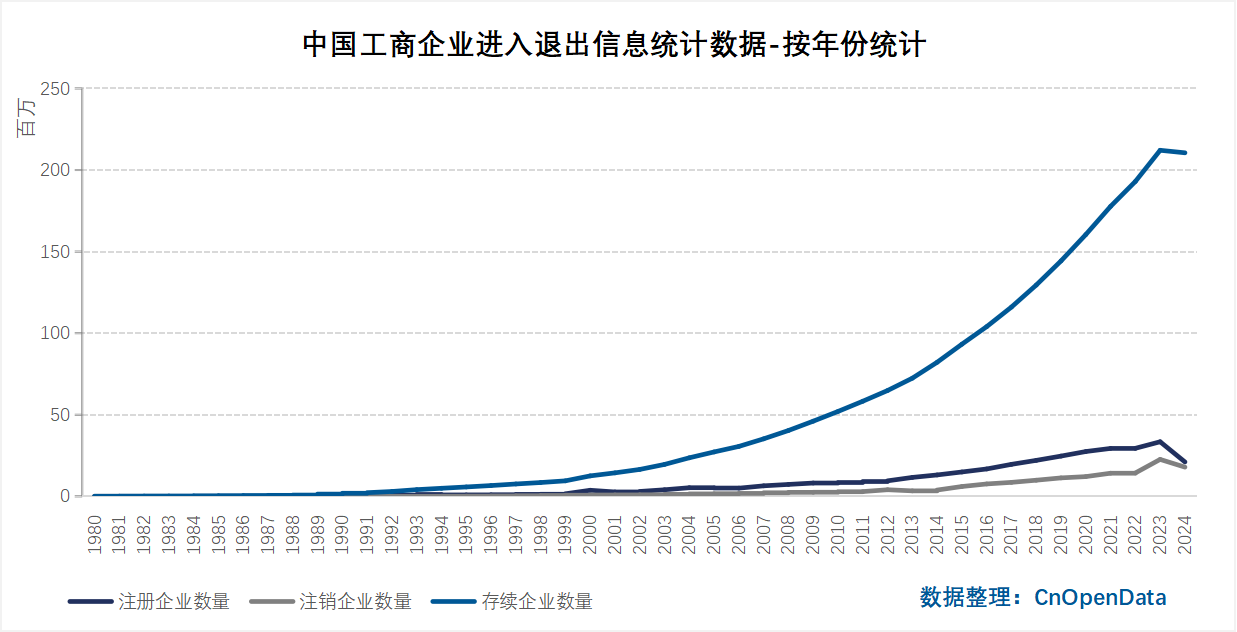
Time Coverage
Partial tables extend through October 2024.
Data Scale
Data Schema Presentation
Table Structure Overview
Due to the complexity of the data schema and numerous sub-branches, this overview displays table names only. Detailed field indicators and sample data are accessible via the module-specific pages on the right.
Basic Information Module
Key Focus Areas Module
Intellectual Property Module
Enterprise Development Module
Operational Status Module
Relevant Literature
- TANG Wei, MAO Kailin, ZHU Ruihua, 2024: "Population Migration and Entrepreneurship: Job Creation Effects of Migrants," Journal of Quantitative & Technological Economics, Vol. 11.
- LI Maolin, WANG Zilu, HE Guanghui, WANG Yukun, 2024: "Fintech Innovation in Banking, Structural Inclusive Effects, and Entrepreneurial Vitality," Management World, Vol. 6.
- LU Yao, WU Jiahe, 2024: "Spillover Effects of Capital Markets on Enterprise Entry and Exit," The Journal of World Economy, Vol. 5.
- ZHAO Ying, LU Yuanping, WANG Xi et al., 2023: "Taxpayer Status Selection and Employment Opportunities: Evidence from Matched Industrial-Commercial and Tax Data," Economic Research Journal, Vol. 9.
- Panle Jia Barwick, Luming Chen, Shanjun Li, Xiaobo Zhang, 2025: "Entry Deregulation, Market Turnover, and Efficiency: China's Business Registration Reform," The Review of Economics and Statistics.
Data Update Frequency
Annual updates.
